The concept of digital twins emerged during the early 2000s in the machinery industry. This was the period when machinery and production systems had begun to digitise. And as I have never worked with machinery or production systems so perhaps that’s why until recently the concept of Digital Twins was unknown to me.
When couple of days back I received an invitation from my department to attend “Inspirational Day about Digital Twins” instantly a holographic image of my digital twin lying on cloud (somewhat similar to the image below) instantly flashed across my mind.
And with that flash, questions like, what is digital twin made of (tools, technologies)? Is it an identical twin or fraternal? If this digital twin is lying on the cloud then who else has access to it? Can my digital twin grow with me? How can having a digital twin impact on real me? started appearing in my mind. But before I would get little too carried away by these questions I rather found it more sensible to start with finding the definition of digital twin for verifying as if digital twin exactly is a twin of a human beings or just a fancy term for another old technical concept. So let me take this opportunity and share my findings with you.
What is Digital Twin?
“Digital Twins are being defined as digital replications of living as well as nonliving entities that enable data to be seamlessly transmitted between the physical and virtual worlds”.
[Source: “Digital Twins: The Convergence of Multimedia Technologies”. IEEE MultiMedia. 25 (2): 87–92 ]
The first part of definition i.e. Digital Twins are replicas of living, validated my assumption for the concept of Digital Twins but the later part intrigued my interest further in concept as it involved the concept of enablement of data transmission between physical entities and virtual worlds.
One thing that became clear by looking into the definition is that the technology behind digital twins covers both living and nonliving i.e. anything from humans to buildings and cities, and systems to processes can have digital twin and the technology can even be expanded further.
As mentioned in the start of article the term has been first tossed somewhere in the early 2000s but it took the hype after it was named as Top 10 Strategic Concepts for Technology in 2017 by Gartner. A year later, Gartner once again named digital twins as a top trend, saying that “with an estimated 21 billion connected sensors and endpoints by 2020, digital twins will exist for billions of things in the near future.”
It is worth looking at how does a technology, that holds such significance and will going to be so readily available very shortly works.
How does Digital Twins Work?
Digital twins integrate the technologies like Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Software Analytics with Spatial Network Graphs (SNG) to create simulation models.
In simple terms, the entity whose digital twin needs to be created undergoes the intensive research and all the relevant data about it is collected. That data is further used to develop a model, this model gets the operational data and environmental data and constantly updates itself. Besides themselves, these models can also reach other systems connected to them and can access historical data and incorporate it into the model and uses it to derive business outcomes. Hence these models can simulate the real world in digital space and can warn us and can predict the failures to reduce maintenance cost and optimise itself.
Digital twin can be both complicated and simple depending upon your choice. The amount of data you use to build and update it, will determine how precisely you are simulating a physical object and how complex or simple a digital twin is.
How Digital Twins are Different From Simulations?
Digital Twins are different from simulations as they are not just models but the whole concept. Digital Twins are intelligent systems which learn using AI and Machine Learning algorithms and sensors technology to learn from different sources including themselves, other machines, the environment they are part of, the human interactions as well as from historical data available.
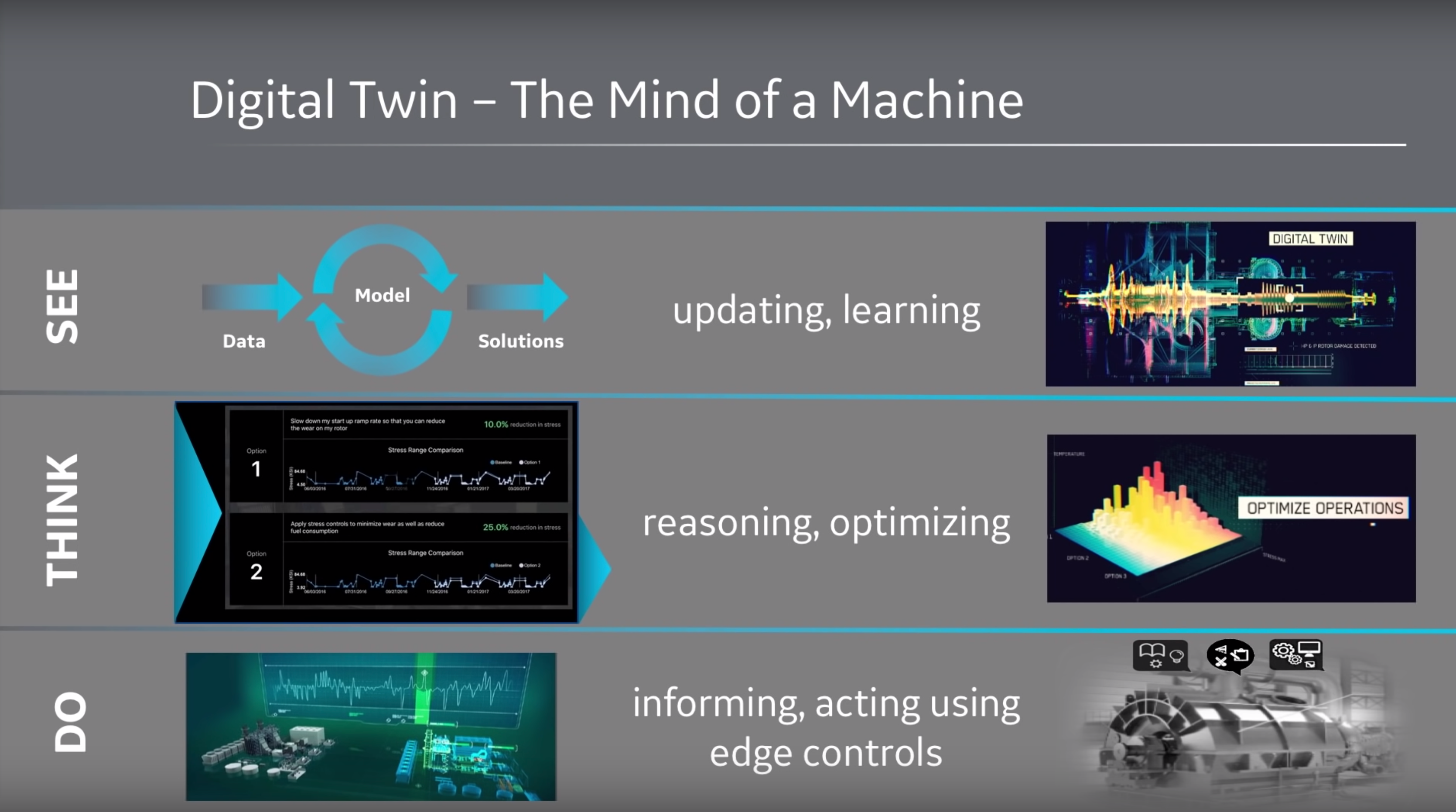
According to Dr Collin J. Parris Vice President Software Research, GE Global Research digital twins work in three steps i.e. See, Think, Do.
See stage is the data-gathering stage where Digital Twin is gathering data about its situation to create a model. During the seeing stage, the model continually learns from its physical counterparts and updates itself so to represent its almost real-time status, position or working condition as in diagnostics, error reports etc.
In Think stage, simulations are run over 1000s of simulations running them over platforms as cloud. In doing so it is looking at the data from other similar physical entities, forecasts to give the 1000s of options and then reasons to choose those options based on the risks and opportunities associated with each choice based on data available for each choice.
The Do stage is all about informing and executing what needs to be done. The information could be the errors and warnings or the suggestions to optimise performance etc and execution is about performing counter tasks to avoid failures or to bring improvements in processes which in turn optimise overall performance.
Where Can We Use Digital Twin Technology?
So the question arises why to create digital replicas or digital twins when the real thing already exists? And in fact, there are more than one answers to these questions. So let us have a look at them one by one.
1- Digital Twins enables in-depth analyses by leveraging big data, IoT and AI solutions.
2- Digital Twin is very useful in identifying and detecting potential issues, faults and troubleshooting opportunities from afar, ultimately preventing downtime and testing new business opportunities, improved customer satisfaction and opportunity for planning future scenarios through simulation and customise production based on customer requirements. Hence digital twins give businesses a view into how the products are performing.
3-It also helps with product differentiation, product quality, and add-on services, too. If you can see how customers are using your product after they’ve bought it, you can gain a wealth of insights. That means you can use the data to, safely eliminate unwanted products, functionality, or components, saving time and money.
4-Digital Twin technology makes it possible to have immediate feedback about the activity in progress and apply eventual corrections in record time. Hence reducing the maintenance cost of connected heavy machines and infrastructure that generates and analyses a large volume of data.
Digital Twin is a big thing for many industries and for my next article I will be looking into Digital Twins and IoT.
Article: A Fascinating Look at Digital Twin