Bring up Artificial Intelligence in a room and people’s minds wander to shiny robots who will take our jobs or a lot of science fiction.
If we look at the Oxford dictionary definition of Artificial Intelligence, this is what we get: ‘the study and development of computer systems that can copy intelligent human behaviour.’
For the majority of society, this means very little, however if you work or are surrounded in the tech industry, you have our personal definitions. The limitation of the definition that Artificial Intelligence is primarily based on computers imitating human intelligence does not give us a broad understanding of what Artificial Intelligence actually is?
What’s the difference between types of AI? What type of AI is Siri? What’s the difference between machine learning and deep learning? We at AI Time Journal believe that the majority of society should have a better understanding of Artificial Intelligence and how it’s part of our everyday lives and this is what this article will go through.
In the world of technology and computer science, Artificial Intelligence relates to human-like intelligence constructed by a computer. It refers to the capability of a computer/machine to imitate the characteristics of the human brain by replicating its intelligence.
However, that still doesn’t really give you a good understanding of what it actually does, right?
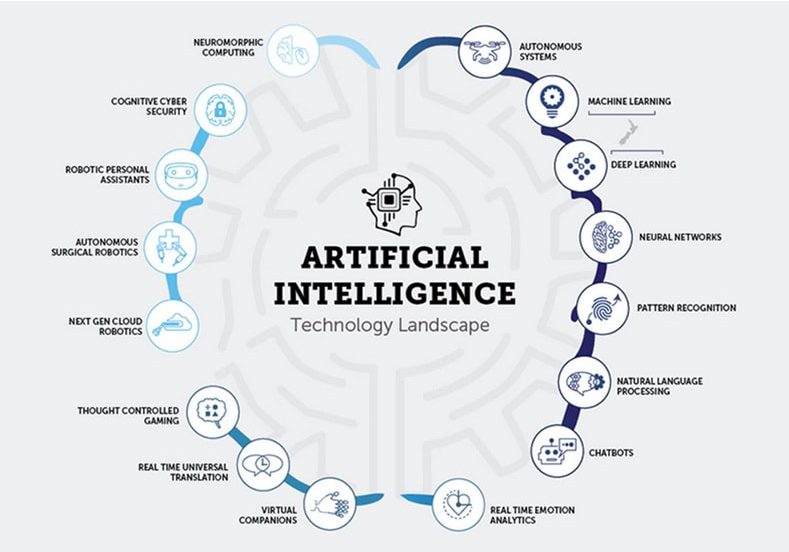
Brief history of AI
Let’s look into the history of AI. In the mid-1950’s, John McCarthy who is known as the father of Artificial Intelligence for creating the terminology of AI. For him, his definition of AI was “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines”. Some may know him for creating Lisp, which is a programming language used in robotics for different types of Internet services. He started working on self-driving cars to create programs that understand the human brain better and imitate the way humans make decisions. Many of us use Cloud computing services, where we can share data between people. This was another of McCarthys innovations.
The surge in the development of Artificial Intelligence is primarily dependent on the access of available large amounts of data and the evolution of technology allowing the data process and manipulation better than humans. Artificial Intelligence can do everything us humans can do, from giving us directions to medical analysis.
Some further examples of AI today are Amazon’s Alexa and Apple Siri who help us create potential links on what we may want to purchase based on our current searches, being able to recognise spam emails whilst also helping us detect fraud.
There are two broad types of Artificial Intelligence:
- Narrow AI
- General AI
Narrow AI
Narrow AI is the type of AI which performs a single take. It’s being able to carry out specific tasks which intelligent systems have been taught without being sophistically programmed, this is why it’s called Narrow AI. To give you a better understanding, it’s Siri for Apple users. Examples of this are self-driving cars and voice recognition to help radiologists pick up tumours.
Machine and Deep Learning
Narrow AI is based on machine learning and deep learning. A better way to understand what you just read, AI is constructed on a set of algorithms which try to imitate human intelligence. Machine learning is one of these algorithms and deep learning is a sub-skill of a machine learning technique.
Machine learning consumes data and uses statistics to better learn the data, in turn improving the ability to solve the task. Machine learning is made up of both supervised and unsupervised learning. Supervised learning learns on a labeled dataset, allowing you to produce outputs based on previous data whereas Unsupervised learning uses unlabeled data to learn on and discover unknown patterns in data.
Deep learning, also known as deep neural learning, is a type of machine learning technique that tries to imitate the human brain by inputting data through a biological inspired neural network which contains a number of hidden layers. Through the hidden layers, the data is processed making connections and creating patterns.
General AI
General AI has a bit more complexity to it and tries to mirror human intellect using its ability to learn and apply the knowledge learnt to solve problems. We are now going through the process of transitioning from Narrow AI to General AI, example natural language processing. In order to achieve this, computer hardware needs to advance in computational power to perform at a better rate.
If you would like to know a bit more about General AI, please check out an Interview we conducted with Charles Simon, CEO and Founder of of FutureAI here.
Examples of AI Application:
Below are some examples of AI applications to give you a better understanding of how it has been implemented:
- Speech recognition: This is the process of enabling a computer to recognise spoken words and have the ability to respond, example; Siri.
- Natural Language Processing: This enables softwares to understand, interpret and generate the human language, example; language translation and email filtering.
- Image recognition: This process can classify text, people and objects as well as moving images. Examples of this are; fingerprint ID system, self-driving cars and face recognition.
These are only a few examples of where AI has evolved and we hope this has helped you on your early journey in the world of Artificial Intelligence and the evolution of technology.
Article: What is Artificial Intelligence? (AI)